Fall 2017 Exam 1 STUDY GUIDE
STUFF FOR EXAM!
- Terms: living fossils, metamorphic, Law of superposition, Cyclops, biomarkers/chemical fossils, functional extinction, taphonomy, E/MSY, LIP, anthropogenic, species diversity, Coelophysis, Gryphon, extinction, carbonization, Baron Georges Cuvier, endocast, ichnofossil, trace fossils, diagenesis, permineralization, replacement, Cambrian explosion, recrystallization, Lagerstatten, Signor-Lipps effect, Lazarus taxa, Geozoic, amniotic egg, the Great Dying, Nicholas Steno, fungal or fern spike, Pangea, Jack Sepkoski, weathering, pedogenesis, Siberian traps.
- Know the geological history chart/terms
- Origin of life, eukaryotes, sex, vascular plants, multi-cellular life, metazoans, reptiles, mammals/birds, flowering plants
- Be able to describe what the graphs (below) are illustrating and what you’d predict from them
- Be able to respond to the short answer questions, such as the following (NOT inclusive!):
1.
What is the typical ‘lifespan” of a species? Draw the shape of this
distribution for species/genera.
2.
How many extinctions do you expect per million-species years?
3.
What is the 6th extinction?
4.
How did Cuvier demonstrate extinction?
5.
Give an example of how a biogeochemical process/cycle influences both the
terrestrial/marine and atmosphere?
6.
What are the ultimate causes of mass extinctions? Difference between
ultimate and proximate causes of extinction?
7.
Name the five Big mass extinctions and when they occurred.
8.
How did oxygen in the atmosphere change? When and by what mechanism?
9.
Examples of trace fossils and information they provide.
10.
What is the ‘Law of superposition’? Diagram how this works.
11.
What are the kill mechanisms behind bolide impact? Glaciation? LIPs?,
12.
Species diversity = O-E. Explain the significance of this.
13.
What is a fossil? How do you become one? How can biotic factors interfere
with the likelihood of an individual becoming a fossil?
14.
What is a true form fossil? How do they occur?
15.
Given some data, draw a stratigraphic range. Draw a spindle diagram.
16.
What is taphonomy? What sorts of biases does this discipline study?
17.
What is the Signor-Lipps effect? What are Lazarus taxa?
18.
How do LIPs cause extinction?
19.
How do you calculate extinction rates (e.g., per taxon extinction, or
taxa per ma)
20.
What went on in the Hadean/Archean Eons?
21.
How can a lowering of sea level contribute to extinctions? What sorts of
taxa are influenced by this? How?
22.
Describe some similarities and differences between the end-Ordovican and
Devonian extinctions
23.
What did the earliest life look like? When did this likely arise?
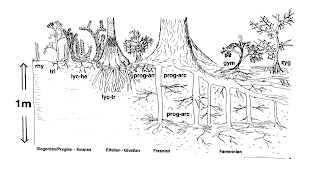
24.
How might the evolution of trees have led to a mass extinction? Describe
the mechanisms.
25.
Do the same factors predispose species to extinction during mass and
background extinctions?
26.
Why was the End-Permian explication so severe? What theories have been
proposed to address this?
27.
Why do paleontologists focus on genera or families rather than species?
28.
What does the presence of fungal/fern spike in the fossil record suggest?
29.
What information does a shift in the relative proportion of 12C
to 13 C provide about ancient ecosystems?
30.
How did the ‘rules of evolution’ change from the Precambrian to the Phanerozoic?






















Comments
Post a Comment